A while ago, I demonstrated how first time programming students can get started in the video below. It’s a bit old , but it gets the job done. You can download the Pascal environment for PC here: Dev-Pascal Install File which can be found here
A while ago, I demonstrated how first time programming students can get started in the video below. It’s a bit old , but it gets the job done. You can download the Pascal environment for PC here: Dev-Pascal Install File which can be found here
Definition: Telecommunication means communication at a distance (tele means “at a distance”). Modern telecommunication is usually timely and employs electronic devices.
Definition: E-mail (electronic mail) is the exchange of computer-stored messages by telecommunication[1]. It can be thought of as the electronic version of traditional mail.
Teacher demonstrates the sending of email:
An email attachment is a digital file that is added to an email message for delivery to the recipient.e.g. a picture, audio file , program file etc
Each user has a unique email address specified by their username at the mail server in the following format:
username@server.topLevelDomain
e.g. JimBob@yahoo.com
Internet email messages consist of two major sections:
The message header must include at least the following fields:
The email address of the originator of the message. This field is sometimes formatted to include a first name and last name, or other alternative formats
The geographical local time and date when the message was sent. This field is almost exclusively generated by the email service provider (e.g Gmail, Hotmail etc)
The email address(es) OF the messages’ main recipient(s).
Carbon Copy. Recipients in this field receive a copy of the email between the sender in From: and the main recipients in To:. The recipients can see all recipients in the and To: and Cc: fields.
This term originated from the use of traditional carbon paper to produce copies of hand written pages.
Short for Blind Carbon Copy. Recipients in this field receive a copy of the email between the sender in From: and the main recipients in To: as well as Cc:. The main difference here is that recipients in the To: and Cc: fields WILL NOT see any recipients specified in Bcc:
A brief summary of the topic of the message. Certain abbreviations are commonly used in the subject, including “RE:” (concerning) and “FW:” (forwarded message).
A forwarded message is a copy of an email sent to a recipient at a later time than the original email.
Updates:
2023 Jan 7th
-Added section for email address format.
[1] https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/e-mail-electronic-mail-or-email
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Comparison of computer systems

© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
The hardware components include the keyboard , monitor , cpu (processor) an the hard drive. In this lesson, we wish to observe the main functions for each component category.
Data processing has a logical organization divided into 4 main steps functions.
Computers input data via input devices, processes the data to produce information which is in turn output to the user via output devices. The results of processing or even the captured data can be stored on storage devices.
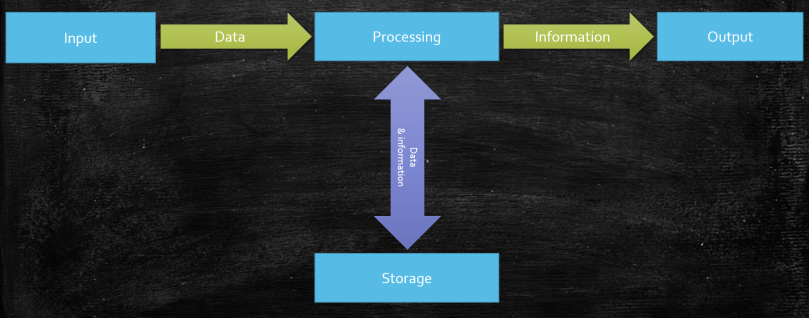
Input : to get data into the computer system
Processing: perform some operation on data as directed by software instructions.
Output: to make the results of processing (information) available to the computer user.
Storage: to store data and information for future use.

© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Computing disciplines are sometimes fundamentally distinct or may differ subtly. The difference among disciplines originates based on the use of computer systems as a tool and for the purpose of further developing the tool.
Computer Technology is the broad use of computers to solve problems.
Information technology is the study and use of computer technology for effective information storage, access, and manipulation; that is, information management.
ICT is an extension of IT, in includes effective information management across all major communication channels including telephone, wired and wireless computer networks.
Computer science is a branch of science which deals with the fundamental principles of computer design and use.
Computer science focuses on computer architecture and how to program computers to make them work effectively and efficiently[1].
[1] Computer Concepts (2011) p514
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Definition: A problem is a required change from the current state of things to a desired future state.
Definition: Computational thinking is use of ideas in a structured manner to solve a problem, such that it can be eventually used to instruct a computer.
Building applications or programs is essential to aiding computer users to perform tasks.
We use computational thinking to analyze problems in order to build applications that solve those problems.
There are four principles that are used to solve problems computationally.
They are:
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Create an algorithm in flowchart AND pseudocode to accomplish the following task:
“output the squares of all numbers from 2 to 75 inclusive”.

The solution was also generated in Flowgorithm and is shown below:

Similar solution generated in Flowgorithm
The solution in PSEUDOCODE is shown below:
Start
For i = 2 to 75
Output i , ” Squared is ” , i * i
EndFor
End
The pascal code for the above algorithm is shown below:

Solution in bloodshed Dev Pascal
Copy-able code:
program Squares;
uses
crt;
var
i:integer;
begin
for i:=2 to 75 do
writeln (i, ‘ squared is ‘ , i*i);
writeln();
writeln(‘Press any key to continue…’);
readkey();
end.
The following is a solution in C#:

Solution created using Visual Studio Community Edition
See here for instructions on setting up Visual Studio to start using C#
Copy-able code:
using System;
namespace Squares
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 75; i++)
Console.WriteLine(i + ” squared is ” + (i * i));
//pause execution here
Console.WriteLine(“press any key to continue….”);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Definition: A protocol set of rules for communication
Definition: VOIP is the protocol which governs voice communication by sending the audio over the internet.
VOIP can be implemented by phone handsets which is connected to a computer network. Some popular apps also allow for VOIP, e.g Skype, Whatsapp, Discord, Telegram etc.
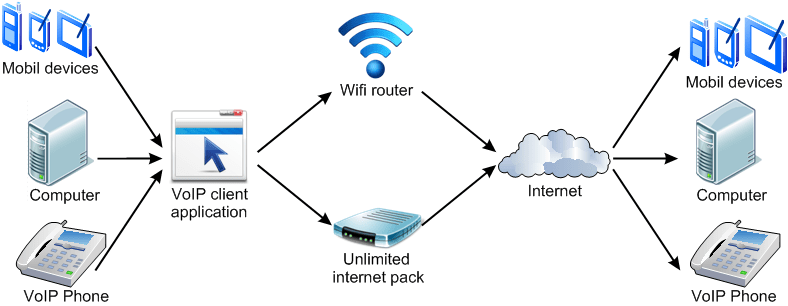
Figure 9 VOIP Implementation (Credit: http://cat5comms.com/landlines-and-voip/)
Some reasons why we use VOIP are:
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
Exercise: block problem
3 blocks ABC rest on a desk. What are the steps to stack B on C on A?
After completing the exercise, continue:
Computational thinking allows for us to arrive at well defined steps based on the tool that we are using.
If a robotic Arm Were used the steps would be:
If we were directing a human, we might arrive at:
You may arrive at an entirely different solution:
Computational thinking allows for us to find General solutions to problems also. For example, if our problem was
“ N blocks rest on a table. Create a stack using all blocks. “
Using a robotic arm , our solution would be:
Note that:
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved
A student reproduced a programming question for me today:
Write a program which accepts 2 integers separated by a space. If the first integer is less than the second integer, output a message stating this fact e.g “The first number is smaller”, else swap the values of both variables which contain the integers respectively.
Before the program exits, print both integers respectively.
A flowchart for the solution is shown below. Note that, input is obtained on separate lines, a limitation of the software used to create the chart, flowgorithm:

Below is a suggested solution written in pascal code:

Copy-able pascal code here:
program swap;
uses crt;
var
num1,num2,temp:integer;
begin
writeln(‘Please enter 2 unequal integers separated by a space…’) ;
//read data separated by a space
readln (num1,num2);
if (num1>num2) then //we swap the numbers using a tempoary varible
begin
temp:=num1;
num1:=num2;
num2:=temp;
end //notice that there is no semicolon on this line.
else//print message
writeln(‘num1 is less than num2’);
writeln();
writeln(num1,’ ‘,num2) ;
writeln(‘Press any key to exit…’);
readkey;
end.
Below is a suggested solution written in c# code (generated by flowgorithm and edited to accept input of the two integers on one line):

Copy-able c# code here:
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int num1, num2, temp;
string anykey;
Console.WriteLine(“Please enter 2 unequal integers separated by a space…”);
//Read line, and split it by whitespace into an array of strings
string[] tokens = Console.ReadLine().Split();
//Parse element 0
num1 = int.Parse(tokens[0]);
//Parse element 1
num2 = int.Parse(tokens[1]);
if (num1 > num2)
{
temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(“num1 is less than num2” + “\n”);
}
Console.WriteLine(num1 + ” ” + num2 + “\n”);
Console.WriteLine(“Press any key to exit.” + “\n”);
anykey = Console.ReadLine();
}
}
© 2018 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved