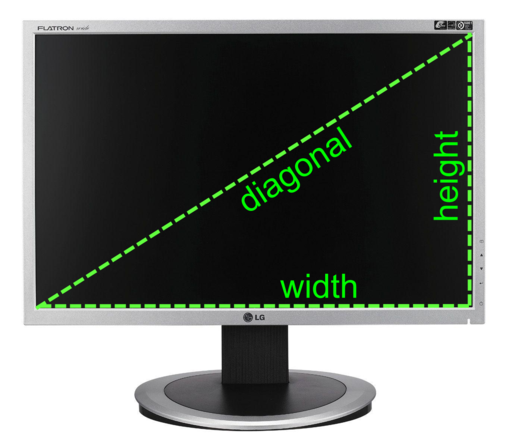
Size
Screen sizes are measured along the diagonal of the screen and is usually quoted in inches. For example, a typical computer monitor or laptop screen may be 15” in size.
Resolution
Screen resolution refers to the quality and level of detail that can be displayed on the screen. The screen is made up of a matrix of individual dots that can be coloured differently. Each dot is know as a picture element or pixel for short.

Example of pixels. Shows a zoomed section of an image to demonstrate how it is made up of pixels.
Maximizing the number of dots in a unit area of the screen will result in a sharper image with more detail , or as we say, a higher resolution image.
A monitor’s screen resolution is denoted as horizontal pixels x vertical pixels. e.g 1920 * 1080
How does Size and Resolution relate to each other?
It’s possible for a monitor with large screen to have a small resolution, to the average person, the screen may display images which are blocky, where the pixels are discernable and the image is not smooth.
It’s also possible to have a very small screen have a high resolution, as in the case of a high end smartphone.
Size and resolution consideration depends on where the screen needed, for example, having a large screen with a low resolution at a train station or airport is feasible since a lot of people can easily view the screen at once , however , we do not require the need to display detailed images, just formatted text or cursive fonts.

On the other side of the spectrum, a graphic artist travelling on a long train ride may opt to get his/her/them/they/us work done on a portable tablet computer which has a small but very high resolution stylus touch screen to allow for fine and detailed designs to be viewed while being created.
Attributions to media used in this post:
florisla, CC BY-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
ed g2s • talk, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
MaedaAkihiko, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
TopSystemsLTD, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
© 2023 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved.
.






