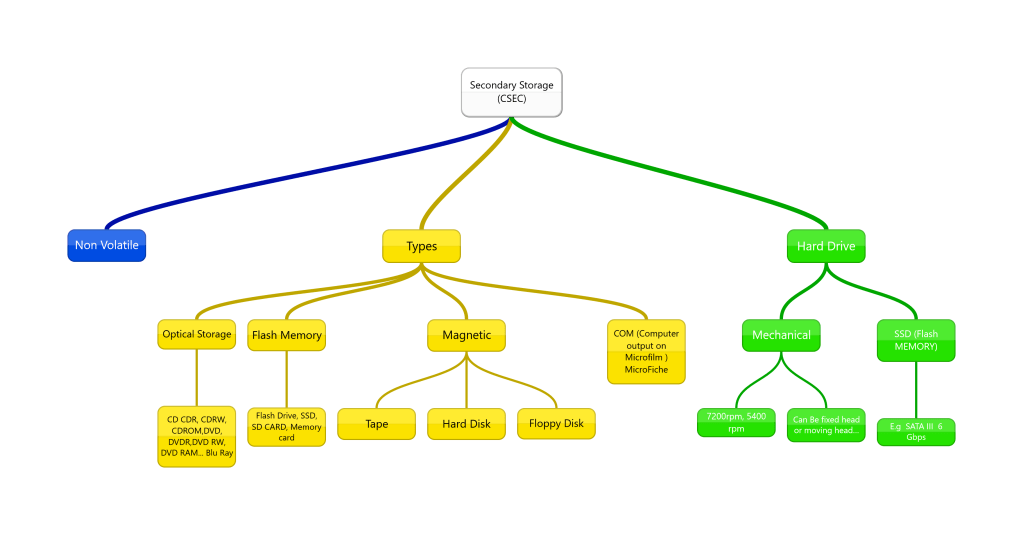
In this post, we build on the menu system shown here:Mini Internal Assessment Example
Screen Shots


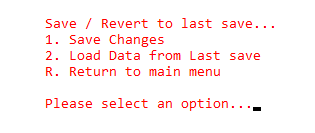
Project organization
Code is split into various C and Header files as shown in the screen capture below:
See the Contents of the code files below:
main.c
/*
This program demonstrates how a menu driven
system can be used to trigger functions used
to maintain a simple library catalog.
Data is loaded to and from a binary file.
Date : 16th November 2019
Author : Vedesh Kungebeharry
*/
#include "MenuSystem.h"
#include "CatalogSystem.h"
//function declarations
void initialization();
void exitProgram();
int main()
{
initialization();
runMainMenu();
exitProgram();
return 0;
}
void initialization()
{
menuInitialization();
loadCatalogFromFile();
}
void exitProgram()
{
saveCatalogToFile();
exitProgramMenu();
}
CatalogSystem.h
#include <stdbool.h>
#ifndef CATALOGSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
#define CATALOGSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
//#include "CatalogSystem.c"
//structures
typedef struct BookStructure
{
char Title [50];
char Author [50];
int Year;
bool isOnLoan;
bool hasData;
} Book;
//function declarations
void printBookByLocation(int location);
void printBook(Book b);
int findBook(char searchQuery[]);
void printAllBooks();
int addBook(Book newBook);
//file function declaration
void saveCatalogToFile();
bool loadCatalogFromFile();
//functions for testing
void setupDummyData();
#endif // CATALOGSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
CatalogSystem.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "CatalogSystem.h"
#define maxSize 1000
//constants
const char catalogFilename[50] = "catalog.bin";
//global variables
Book catalog[maxSize];
int count = 0;
FILE *datafilePtr;
//prints a book stored at a given index in the catalog array
void printBookByLocation(int location)
{
printBook(catalog[location]);
}
void printBook(Book b)
{
if (b.hasData)
{
printf("Title:\t%s\n",b.Title);
printf("Author:\t%s\n",b.Author);
printf("Year:\t%d\n",b.Year);
printf("Loaned? : \t%s\n\n",b.isOnLoan?"Yes":"No");
//printf("hasData: \t%s\n\n", b.hasData?"Yes":"No");
}
else
{
printf("\nNo book found at current index location...\n");
}
}
int addBook(Book newBook)
{
newBook.hasData=true;
catalog[count]=newBook;//place book in next
//empty location in the array
count++;//increment count to point to the
//next empty location.
return count-1;
}
void printAllBooks()
{
if(count==0)
{
printf("\nNo books in catalog\n");
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i<count;i++)
printBook(catalog[i]);
}
}
//finds a book by searching for titles that contain a substring of the query.
//this function finds the first positive result only
int findBook(char searchQuery[])
{
for( int i = 0; i<count; i++)
{
char currentBookTitle[50];
char lowercaseSearchQuery[50];
strcpy(currentBookTitle,catalog[i].Title);
strcpy(lowercaseSearchQuery,searchQuery);
strlwr(currentBookTitle);
strlwr(lowercaseSearchQuery);
if(strstr(currentBookTitle, lowercaseSearchQuery))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void saveCatalogToFile()
{
datafilePtr = fopen(catalogFilename,"wb");
if (datafilePtr == NULL)
{
//unable to create file
printf("Error creating file to save data\n");
exit(1);
}
else
{
fwrite(&count,sizeof(int),1,datafilePtr) ;
for(int i = 0; i<count; i++)
{
fwrite(&catalog[i],sizeof(Book),1,datafilePtr) ;
}
}
fclose(datafilePtr);
}
bool loadCatalogFromFile()
{
datafilePtr = fopen(catalogFilename,"rb");
if (datafilePtr == NULL)
{
//unable to create file
printf("Datafile not found...Catalog empty\n");
printf("A new save file will be created during exit or manual save....\n");
return false;
}
else
{
fread(&count,sizeof(int),1,datafilePtr);
for(int i = 0; i<count; i++)
{
fread(&catalog[i],sizeof(Book),1,datafilePtr) ;
}
}
fclose(datafilePtr);
return true;
}
void setupDummyData()
{
Book a=
{
.Title = "ATitle",
.Author = "AAuthor",
.Year = 2006 ,
.isOnLoan=false
};
Book b=
{
.Title = "BTitle",
.Author = "BAuthor",
.Year = 2006 ,
.isOnLoan=false
};
Book c=
{
.Title = "CTitle",
.Author = "CAuthor",
.Year = 2006 ,
.isOnLoan=false
};
addBook(a);
addBook(b);
addBook(c);
saveCatalogToFile();
}
MenuSystem.h
#ifndef MENUSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
#define MENUSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
//function declarations
void menuInitialization();
void showMainMenu();
void showSaveLoadMenu();
void runMainMenu();
void runSaveLoadMenu();
void pause();
void printAllBooksUserInteraction();
void AddNewBookUserInteraction();
void exitProgramMenu();
void SaveLoadUserInteraction();
void ClearConsoleToColors(int ForgC, int BackC);
void SetColor(int ForgC);
#endif // MENUSYSTEM_H_INCLUDED
MenuSystem.c
#include <time.h> // for pause()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h> //for getch()
#include <string.h>
#include <windows.h> //for SetColor()
#include "MenuSystem.h"
#include "CatalogSystem.h"
/*See: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29574849/how-to-change-text-color-and-console-color-in-codeblocks
system("Color F0");
Letter Represents Background Color while the number represents the text color.
0 = Black
1 = Blue
2 = Green
3 = Aqua
4 = Red
5 = Purple
6 = Yellow
7 = White
8 = Gray
9 = Light Blue
A = Light Green
B = Light Aqua
C = Light Red
D = Light Purple
E = Light Yellow
F = Bright White
*/
//global static variables
char choice;
/*
*initialize all instance variables and arrays here
*
*/
void menuInitialization()
{
choice = '_';
}
//displays the main menu and accepts input
void runMainMenu()
{
int pauseDuration = 2000;
int sentinel=0;//used to break out of our menu loop
while (sentinel>=0)//loop menu here
{
showMainMenu();//display menu text
choice = getch();//get a character from the input buffer
system("@cls");// clear screen after getting input
switch (choice)//based on the choice take the desired action
{
case '1': printf("\nList all books\n");
printAllBooksUserInteraction();
break;
case '2': printf("\nAdd a new book...\n");
AddNewBookUserInteraction();
break;
case '3': SaveLoadUserInteraction();
break;
case 'q': printf("\nYou chose to quit\n");
sentinel=-1;//update the sentinel so that looping will cease
break;
case 'Q': printf("\nYou chose to quit\n");//cease if upper case
sentinel=-1;
break;
default:
printf("\nYou have entered an option that is not in the menu\n");
pause(pauseDuration);
break;
}
if(sentinel>=0)//if we have continued regular execution , continue looping
{
system("@cls");//clear last screen
}
}
}
//shows and accepts input for the math sub menu
void runSaveLoadMenu()
{
int pauseDuration = 2000;
int sentinel=0;
while (sentinel>=0)
{
showSaveLoadMenu();//show options
choice = getch();//get a character from the input buffer
system("@cls");//clear screen
switch (choice)
{
case '1': printf("\n\tSaving All Changes...\n");
saveCatalogToFile();
printf("\n\tSaving Complete...\n");
system("pause");
break;
case '2': printf("\n\tLoading last save...\n");
if(loadCatalogFromFile())//if a catalog datafile exists....
printf("\n\tLoading Complete...\n");
system("pause");
break;
case 'r': //printf("\n\tYou chose to quit\n");
sentinel=-1;
break;
case 'R': //printf("\n\tYou chose to quit\n");
sentinel=-1;
break;
default:
printf("\n\tYou have entered an option that is not in the menu\n");
printf("\n\tReturning to the save menu in %.2lf seconds\n",pauseDuration/1000.00);
pause(pauseDuration);
break;
}
system("@cls");
}
}
void showMainMenu()
{
int animationDelayMS=50;
system("color F1");//set background color to bright white
SetColor(13);//change foreground color of text
//Ascii art generated at:http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&h=1&v=1&f=Doom&t=Main%20Menu%20
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("___ ___ _ ___ ___ \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("| \\/ | (_) | \\/ | \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("| . . | __ _ _ _ __ | . . | ___ _ __ _ _ \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("| |\\/| | / _` || || '_ \\ | |\\/| | / _ \\| '_ \\ | | | | \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("| | | || (_| || || | | | | | | || __/| | | ||  | \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\\_| |_/ \\__,_||_||_|
| \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\\_| |_/ \\__,_||_||_|  \\_| |_/ \\___||_|
\\_| |_/ \\___||_|  \\__,_| \n");
SetColor(3);;//change foreground color of text
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\n1. List all books in Catalog\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("2. Add a new book\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("3. Manually Save or Revert to last save\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("Q. Quit \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\nPlease select an option...");
}
void showSaveLoadMenu()
{
int animationDelayMS=100;
SetColor(12);
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\tSave / Revert to last save...\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\t1. Save Changes\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\t2. Load Data from Last save\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\tR. Return to main menu \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\tPlease select an option...");
}
//pauses execution
void pause(int milliseconds)
{
clock_t now = clock();
while(clock()< now+milliseconds);
}
void exitProgramMenu()
{
printf("\nExiting program in 2 seconds...\n");
pause(2000);
}
void printAllBooksUserInteraction()
{
printf("\nPrinting all books\n");
printAllBooks();
system("Pause");
}
void SaveLoadUserInteraction()
{
runSaveLoadMenu();
}
void AddNewBookUserInteraction()
{
char theTitle[50];
char theAuthor[50];
int theYear;
Book newBook;
printf("\nEnter the Book's Title...\n");
fflush(stdin);
gets(theTitle);
printf("\nEnter the Author's Name...\n");
gets(theAuthor);
printf("\nEnter Year\n");
scanf(" %d",&theYear);
strcpy(newBook.Title,theTitle);
strcpy(newBook.Author,theAuthor);
newBook.Year=theYear;
newBook.isOnLoan=false;
int catalogLocation = addBook(newBook);
SetColor(0);
printf("\nNew Book Created:\n");
printBookByLocation(catalogLocation);
system("pause");
}
//See:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29574849/how-to-change-text-color-and-console-color-in-codeblocks
void ClearConsoleToColors(int ForgC, int BackC)
{
WORD wColor = ((BackC & 0x0F) << 4) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
//Get the handle to the current output buffer...
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
//This is used to reset the carat/cursor to the top left.
COORD coord = {0, 0};
//A return value... indicating how many chars were written
// not used but we need to capture this since it will be
// written anyway (passing NULL causes an access violation).
DWORD count;
//This is a structure containing all of the console info
// it is used here to find the size of the console.
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//Here we will set the current color
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//This fills the buffer with a given character (in this case 32=space).
FillConsoleOutputCharacter(hStdOut, (TCHAR) 32, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
FillConsoleOutputAttribute(hStdOut, csbi.wAttributes, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count );
//This will set our cursor position for the next print statement.
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hStdOut, coord);
}
return;
}
//See:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29574849/how-to-change-text-color-and-console-color-in-codeblocks
void SetColor(int ForgC)
{
WORD wColor;
//This handle is needed to get the current background attribute
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//csbi is used for wAttributes word
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//To mask out all but the background attribute, and to add the color
wColor = (csbi.wAttributes & 0xF0) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
}
return;
}
\\__,_| \n");
SetColor(3);;//change foreground color of text
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\n1. List all books in Catalog\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("2. Add a new book\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("3. Manually Save or Revert to last save\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("Q. Quit \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\nPlease select an option...");
}
void showSaveLoadMenu()
{
int animationDelayMS=100;
SetColor(12);
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\tSave / Revert to last save...\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\t1. Save Changes\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\t2. Load Data from Last save\n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\tR. Return to main menu \n");
pause(animationDelayMS);printf("\n\tPlease select an option...");
}
//pauses execution
void pause(int milliseconds)
{
clock_t now = clock();
while(clock()< now+milliseconds);
}
void exitProgramMenu()
{
printf("\nExiting program in 2 seconds...\n");
pause(2000);
}
void printAllBooksUserInteraction()
{
printf("\nPrinting all books\n");
printAllBooks();
system("Pause");
}
void SaveLoadUserInteraction()
{
runSaveLoadMenu();
}
void AddNewBookUserInteraction()
{
char theTitle[50];
char theAuthor[50];
int theYear;
Book newBook;
printf("\nEnter the Book's Title...\n");
fflush(stdin);
gets(theTitle);
printf("\nEnter the Author's Name...\n");
gets(theAuthor);
printf("\nEnter Year\n");
scanf(" %d",&theYear);
strcpy(newBook.Title,theTitle);
strcpy(newBook.Author,theAuthor);
newBook.Year=theYear;
newBook.isOnLoan=false;
int catalogLocation = addBook(newBook);
SetColor(0);
printf("\nNew Book Created:\n");
printBookByLocation(catalogLocation);
system("pause");
}
//See:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29574849/how-to-change-text-color-and-console-color-in-codeblocks
void ClearConsoleToColors(int ForgC, int BackC)
{
WORD wColor = ((BackC & 0x0F) << 4) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
//Get the handle to the current output buffer...
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
//This is used to reset the carat/cursor to the top left.
COORD coord = {0, 0};
//A return value... indicating how many chars were written
// not used but we need to capture this since it will be
// written anyway (passing NULL causes an access violation).
DWORD count;
//This is a structure containing all of the console info
// it is used here to find the size of the console.
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//Here we will set the current color
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//This fills the buffer with a given character (in this case 32=space).
FillConsoleOutputCharacter(hStdOut, (TCHAR) 32, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count);
FillConsoleOutputAttribute(hStdOut, csbi.wAttributes, csbi.dwSize.X * csbi.dwSize.Y, coord, &count );
//This will set our cursor position for the next print statement.
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hStdOut, coord);
}
return;
}
//See:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29574849/how-to-change-text-color-and-console-color-in-codeblocks
void SetColor(int ForgC)
{
WORD wColor;
//This handle is needed to get the current background attribute
HANDLE hStdOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
CONSOLE_SCREEN_BUFFER_INFO csbi;
//csbi is used for wAttributes word
if(GetConsoleScreenBufferInfo(hStdOut, &csbi))
{
//To mask out all but the background attribute, and to add the color
wColor = (csbi.wAttributes & 0xF0) + (ForgC & 0x0F);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hStdOut, wColor);
}
return;
}
© 2020 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved.