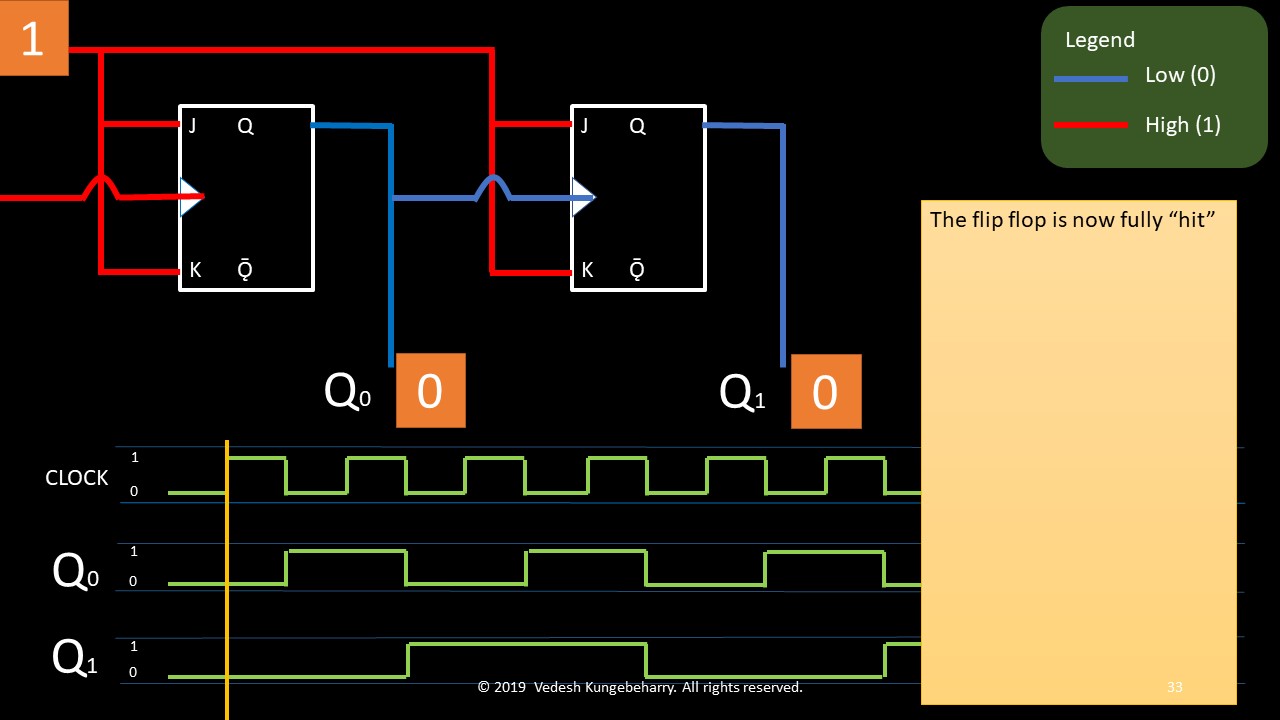
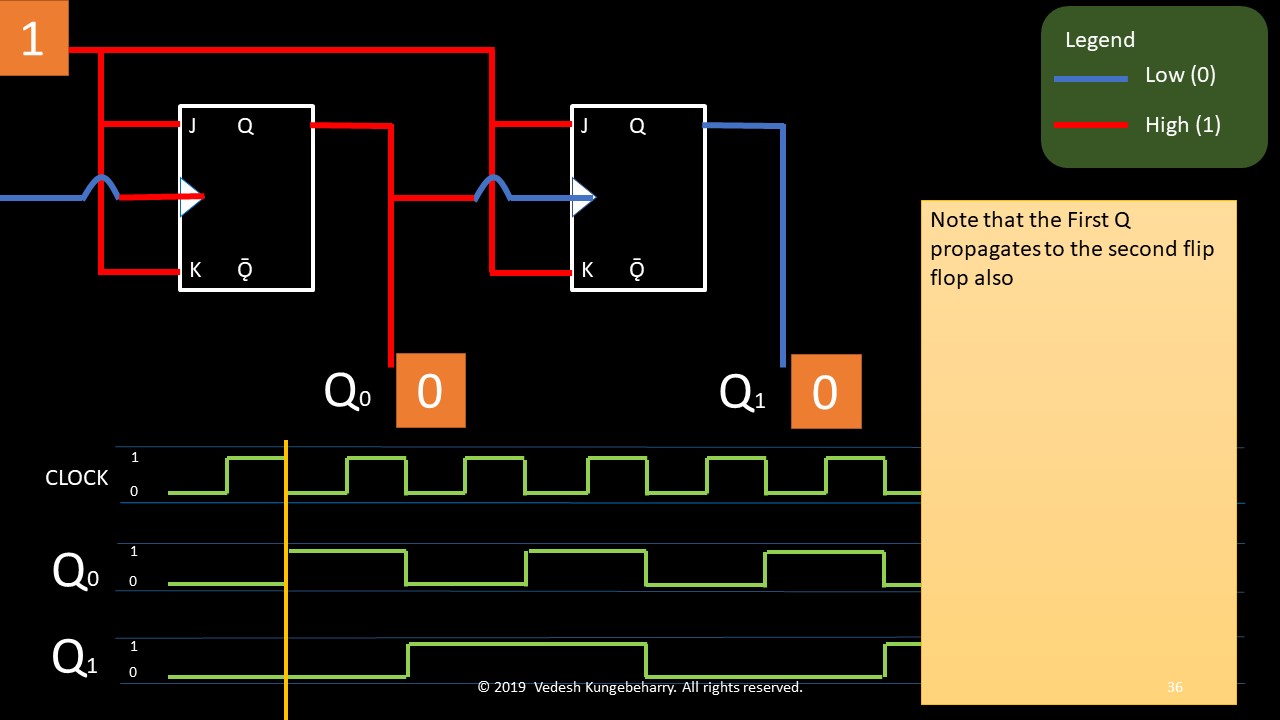
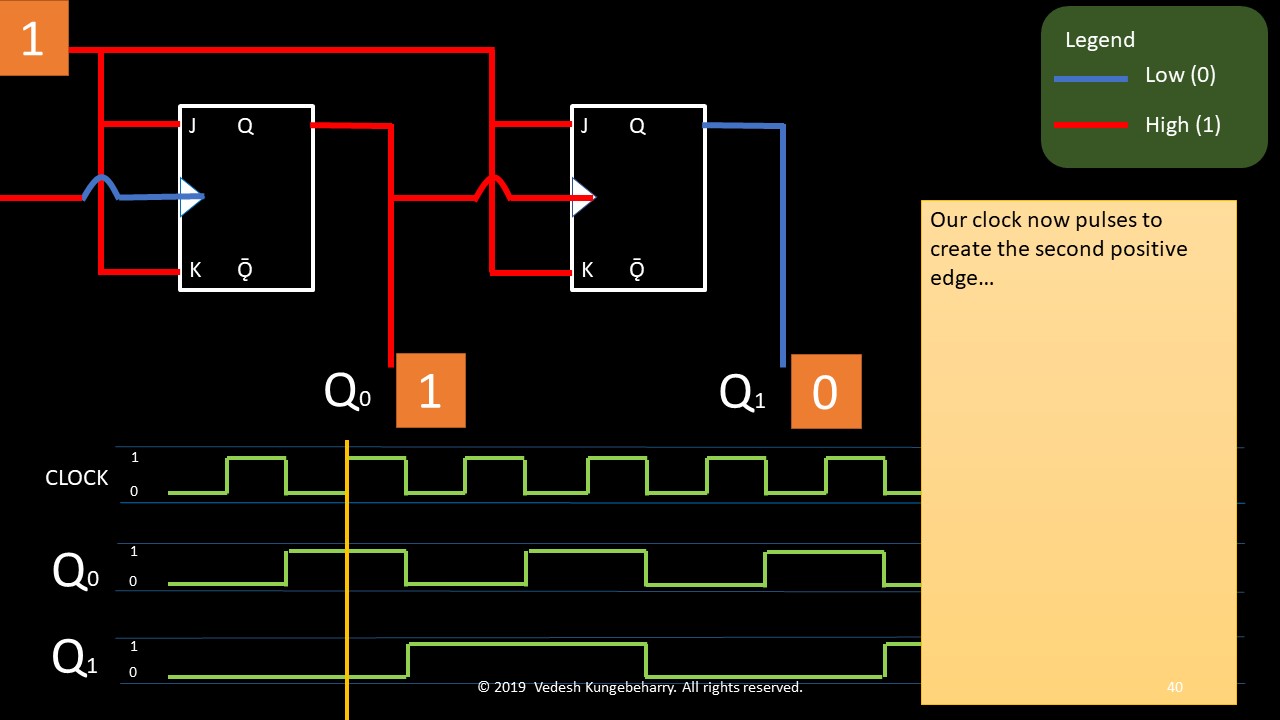
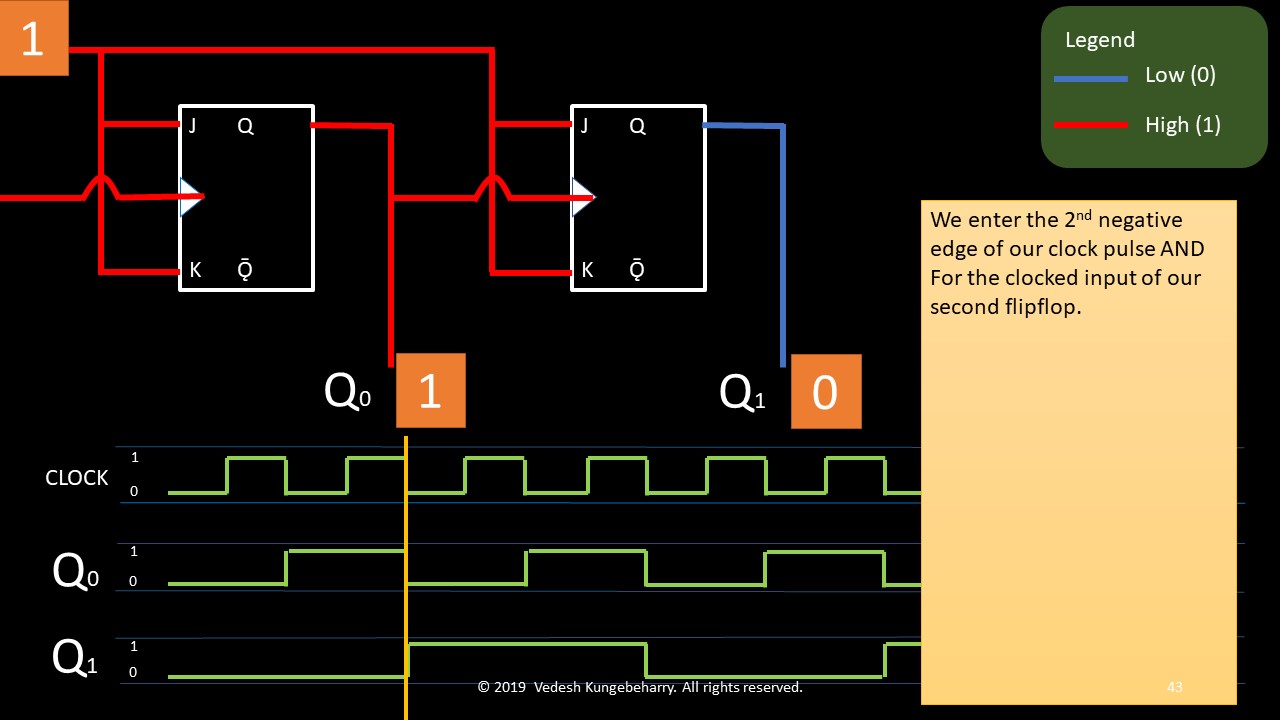
Having studied the principle of a stack, we will list the principle of operation for a queue:
A queue models a real-life queue, for example, a queue (line) of people in a cafeteria waiting to order and pay for food.
The queue (line) of people can be thought of as a list with a :
Head or Front– the first person in the line, and the first to be served.
Tail or End – the last person in the line and the last to be served.
Every time an lunch order is processed, the head of the queue leaves the line, the entire line moves up , and the next person becomes the new head.
The queue ADT consists of a list of items and at least 3 reference variables which keep track of the location of the head, tail and the size of the queue. Operations on the queue are shown below:
| Operation | Explanation | Example |
| Add(..) or Enqueue(..) | Adds/Enqueues an item to the end of the queue and updates the tail to point to the newly added item. if the queue is full, the item is not added and an error message displayed. If the queue is empty, add the new item at the head. In this case the head and tail point to the newly added item. | A person joins the end of the line at the cafeteria. If the line is full, the person cannot enter the line. If the line is empty, the person goes straight to the head, i.e the cash register. |
| Remove(..) or Dequeue(..) | Removes/Dequeues and returns the item at the head of the queue. If the que is empty, the remove operation fails , an error message is displayed. An appropriate dummy/null value is returned. | Accept payment from the person at the cash register and send them on their way. If there are more people in the line, the line moves up and the person at the front of the line is at the cash register. |
| Peek(..) | returns the item at the head of the queue. If the que is empty, the peek operation fails , an error message is displayed. An appropriate dummy/null value is returned. | |
| Size(…) | Returns the size of the queue | |
| IsEmpty() | Returns true if the queue is empty, i.e, size==0 |
Characteristics of a Queue
In creating a coded implementation of a queue using an array, we observe the following characteristics:
State:
| Variable | Description | Value at initialization |
| size | Integer to keep track of the size f the queue. | 0 |
| head | Integer to keep track of the front of the queue. This value stores the array index of the head/front | 0 |
| tail | Integer to keep track of the tail/end of the queue. This value stores the array index of the tail/end | -1 |
| MAX_SIZE | This stores he maximum size of the array; the array length | Sufficiently large, chosen by the programmer. |
Behavior:
Items are added/enqueued using the tail index, items are removed/dequeued using the head index.
During the enqueue operation
If the queue is full
Cannot add, display error message
Else
Increment tail index
Place new data at tail index
Increment size
During the dequeue Operation
If the queue is empty
Display error message, return dummy value e.g -999
Else
Store the data that was at the head in a new variable, X
Increment the head index
Decrement size
Return X
During the Peek Operation
If the queue is empty
Display error message, return dummy value e.g -999
Else
Return the data stored at head index
( updated – 14th October 2020)
© 2020 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved