Parse trees are generated for each expression.
e.g for the code
Line 1: Real D,b,a,c;
Line 2: D= b*b – 4*a*c;
The tokens making up the line 2 (shown below)….
| D | = | b | * | b | – | 4 | * | a | * | c | ; |
…will generate the following tree:
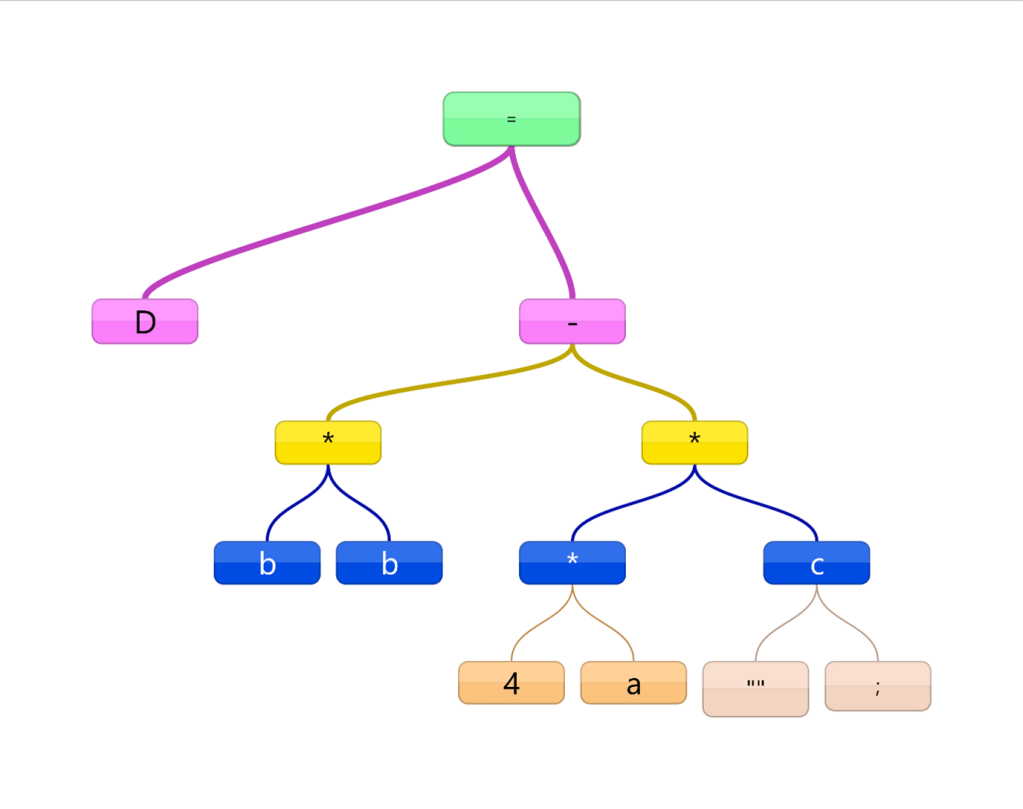
(Note that “” is a null left child of C)
This tree can now be checked for structural errors related to the grammatical rules of the language.
This tree is stored for use in generating the intermediate code and for error checking in semantic parsing.
Demonstration: Teacher uses an inorder traversal to regenerate the original code statement from the tree.
Examples of Syntax errors in C
| Example | Description/Explanation |
int a = 5 | Missing semicolon at the end of the statement. |
if (a < 5) { int b = 0; | Missing closing brace } for the if statement block. |
for (int i = 0 i < 10; i++) | Missing semicolon in the for loop declaration. |
printf("%d", a, b); | Mismatch in the number of arguments in printf. |
int array[5 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; | Syntax error in array initialization (should be array[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};). |
while(a < 5) | Missing opening or closing braces for the while loop body. |
int x = (2, 3); | Incorrect use of the comma operator in assignment. |
© 2024 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved.
