In the previous example we used statements as propositions. Computer logic is accomplished by using logic gates as building blocks. A logic gate is a physical circuit which has electrical inputs and usually a single output.
Used in truth tables, we label each input and use truth values to represent weather or not an input is on or off.
We use the value true , T , 1 to represent on and false , F , 0 to represent off.
Sometimes, On is refered to as a high voltage and off is referred to as a low or no voltage.
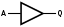
The most common gates are shown in the table below:
|
Gate |
AND |
OR |
NOT |
NAND |
NOR |
XOR |
|
|
Symbol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inputs |
|
||||||
|
A |
B |
Q=AB |
Q=A+B |
Q = A |
Q= AB |
Q= A+B |
Q= A ⊕ B |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Description |
Outputs 1 when all inputs are 1 |
Outputs 1 when ANY input is a 1 |
Inverts the input |
Outputs 0 where all inputs are 1 |
Outputs 1 then both inputs are 0 |
Outputs 1 when exactly one input is 1 |
|
|
Outputs 0 otherwise |
Outputs 0 otherwise |
|
Outputs 1 otherwise |
Outputs 0 otherwise |
Outputs 0 otherwise |
||
Typing the mathematical notation into most word processors can be challenging. Sometimes these worded expressions or symbols are used :
| Gate | Worded expression | Symbol Expression |
|---|---|---|
| AND | A AND B | A^B |
| OR | A OR B | A v B |
| NOT | NOT A | ~A |
| NAND | NOT( A AND B) | ~(A^B) |
| NOR | NOT (A OR B) | ~(A v B) |
| XOR | A XOR B | A ∨ B |
© 2021 Vedesh Kungebeharry. All rights reserved.






[…] Logic Gates – Formal Introduction Multiplexers […]
LikeLike